Comparing Three-Phase Induction Motors and Servo Motors, Which Is the Better Choice?
In the field of modern industrial manufacturing, motors are the core of driving equipment and there are many types. Among them, three-phase induction motors and servo motors are two common choices. They have obvious differences in performance, application and advantages. This article will analyze the two from several aspects so that you can better understand the advantages and disadvantages of three-phase induction motors and servo motors in CNC lathes.
1. Working principle
Three-phase induction motor is one of the common drive motors for CNC lathes. They use the rotating magnetic field generated by the three-phase AC power supply to generate rotational force. When current passes through the stator windings of a motor, it induces an electromotive force in the rotor, thereby producing torque, causing the motor to rotate. Three-phase asynchronous motors usually use open-loop control.
The structure of three-phase Induction motor
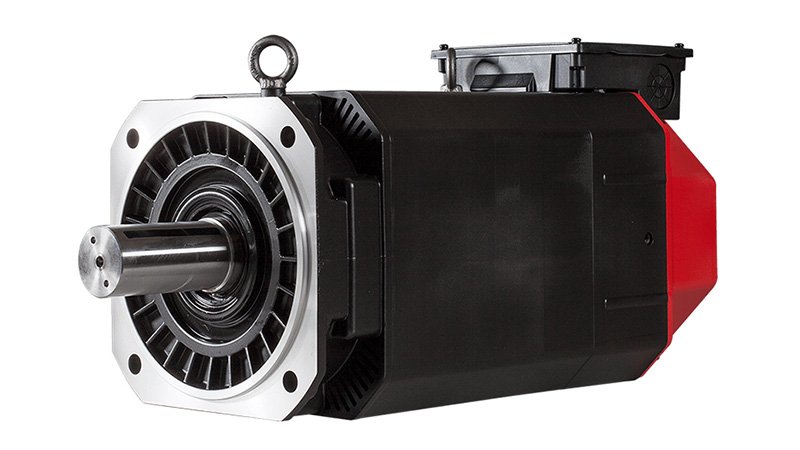
Servo motors represent another common type of driving motor in CNC lathes, typically powered by a direct current source. Servo motors employ a closed-loop control system.
Fanuc Servo Motors
2. Control Precision:
Three-phase induction motors: Control precision is limited due to open-loop control, making precise positioning and speed control difficult.
The servo motor adopts closed-loop control, which can achieve precise position, speed and force control, with higher control accuracy and stability.
Yaskawa Servo Motors
3. Response Speed:
Three-phase induction motors have a slow response speed and are difficult to meet applications with rapidly changing requirements.
The servo motor responds quickly and can adjust the output in real time, making it suitable for scenarios that require high response speed.
4. Dynamic Performance:
Three-phase asynchronous motors have poor dynamic performance and may not be able to meet high-speed and high-precision motion requirements.
Servo motors have excellent dynamic performance, can quickly realize complex motion control, and are suitable for precision machining and high-speed machining scenarios.
5. Load adaptability:
Three-phase induction motors have poor adaptability to load changes and are prone to problems such as stalling and vibration.
Servo motors have good load adaptability and can work stably under different loads to ensure processing quality and stability.
6. Cost and Complexity:
Three-phase induction motors usually have lower cost and simple control systems and are suitable for some applications that do not require high control accuracy.
Servo motors are generally more expensive and are more common in applications that require high precision and dynamic performance. Their control systems are relatively complex, but they can achieve more advanced control functions.
Fanuc Servo Motors
In conclusion, servo motors exhibit superior control precision, response speed, dynamic performance, and load adaptability compared to three-phase induction motors. Their closed-loop control systems enable real-time adjustment of motor output, ensuring stability and precision during machining processes. Especially in the modern era of intelligent manufacturing, where precision and dynamic performance are critical, servo motors shine. Therefore, Smartlathe lathes have adopted servo motors as the standard driving device across our product line, offering users higher precision and efficiency in machining solutions and delivering a superior machining experience.