Plane Definitions of G17, G18, and G19
1. Definition of the G17 Plane
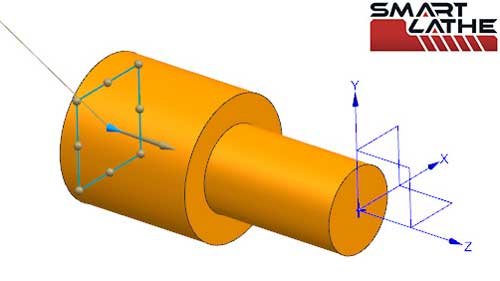
G17 is used to specify the XY plane as the machining plane, performing operations in the plane formed by the X and Y axes.
2. Definition of the G18 Plane
G18 specifies the XZ plane as the machining plane, with machining operations occurring in the plane formed by the X and Z axes.
3. Definition of the G19 Plane
G19 specifies the YZ plane as the machining plane, performing operations in the plane formed by the Y and Z axes.
4. How to Use G17, G18, and G19
The drilling cycle calls the G17 code, setting the XY plane as the machining plane.
The turning cycle calls the G18 code, setting the XZ plane as the machining plane.
The milling cycle calls the G19 code, setting the YZ plane as the machining plane.
5. Functions of G17, G18, and G19
These three commands restrict tool movement to the specified plane, thereby preventing incorrect plane selection during machining, which could otherwise lead to tool collision or workpiece damage. Therefore, using the G17, G18, and G19 codes is essential for ensuring machining quality and safety.
6. Precautions When Using G17, G18, and G19
Upon powering on the machine system, the default plane is the XZ plane, specified by the G18 code.
Once a plane is specified by G17, G18, or G19, only circular interpolation and tool nose radius compensation can occur in that plane, as they are modal commands.